Primary tonsillar Ewing sarcoma in young adult: A rare tumor at an uncommon site
CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 · Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 2014; 35(01): 122-123
DOI: DOI: 10.4103/0971-5851.133743

|
Publication History
Article published online:
19 July 2021
© 2014. Indian Society of Medical and Paediatric Oncology. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.)
Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A-12, 2nd Floor, Sector 2, Noida-201301 UP, India
Sir,
Extraosseous Ewing sarcoma is a rare malignant small round cell tumor that can potentially occur in any soft-tissue location. Common sites for Ewing sarcoma include lower extremities, paravertebral area of spine, retroperitoneum and chest wall. In head and neck regions, rarely extraosseous Ewing sarcoma from soft-tissue of nose, eyelid, nasopharynx, parotid gland, scalp and parapharyngeal spaces have been reported.[1] We report an unusual case of extraosseous Ewing sarcoma of tonsil.
A 25-year-old male patient presented with 3 months history of dysphagia. The primary physician noted asymmetrical growth of left tonsil and was prescribed antibiotics with a presumptive diagnosis of tonsillitis. The symptoms persisted and he presented in emergency department at our hospital with odynophagia. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) scan of neck revealed 4 cm mass in tonsillar fossa extending into anterior tonsillar pillar, posterior oropharyngeal wall and parapharyngeal spaces [Figure 1a]. CECT scan of chest and abdomen showed multiple nodular lesions in both lungs [Figure 1b] and two metastatic lesions in left lobe of liver. An emergency tracheostomy was done and biopsy from tonsillar mass revealed sheets of regular, round to oval, small, undifferentiated cells [Figure 1c] which were immunopositive for CD99, negative for desmin, myogenin, leucocyte common antigen, CD34, chromogranin, synaptophysin, bcl-2, epithelial membrane antigen and pan-cytokeratin [Figure 1d]. This was consistent with extraosseous Ewing sarcoma although we were not able to perform the test for chromosomal translocation t(11;22). Bone scan revealed multiple bone metastases while the bone marrow biopsy did not reveal any tumor deposits. He was started on combination chemotherapy including vincristine, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide alternating with ifosfamide and etoposide with palliative intent. Post 4 cycles of chemotherapy, response evaluation revealed stable disease. He was continued on chemotherapy but died due to disease progression after 6 cycles.
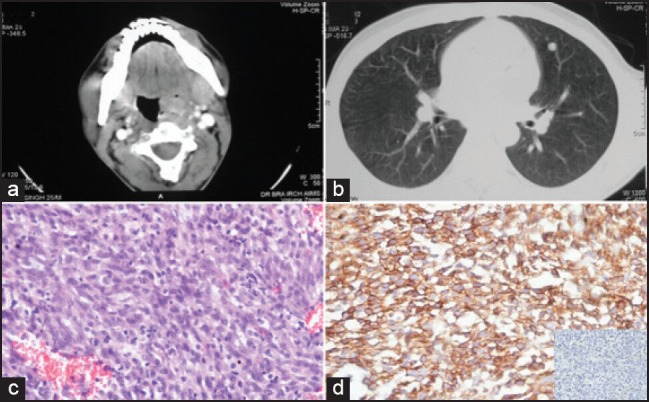
| Figure 1:Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) scan of neck revealed well-defined homogenous soft-tissue mass 4 cm mass in tonsillar fossa extending into anterior tonsillar pillar and oropharyngeal wall (a); CECT scan of chest showed nodular lesions in right upper lobe of lung (b); biopsy of tonsil showing a sheet of regular, malignant round small undifferentiated cells with frequent mitoses (H and E, ×200) (c); tumor cells show diffuse membranous immunopositivity for mic-2. (H and E, ×400) while they are immunonegative for bcl-2 (inset) (d)
Unilateral tonsillar enlargement is considered to be a sign of malignancy. Primary malignant tumor of tonsil represents 10% of oral cavity neoplasms. The most common malignancy of tonsil are squamous cell carcinoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma and rare tumors of tonsil include extramedullary plasmacytoma, Hodgkin lymphoma and metastatic deposits.[2] There has been one previous report of non-metastatic tonsillar Ewing sarcoma in a 75-year-old male.[3] The above case is the first case of tonsillar Ewing sarcoma presenting with metastases and is an alert for head and neck physicians and teen and young adult oncologists to be aware of this rare tumor at this uncommon site.
References
- Ng SH, Ko SF, Cheung YC, Wong HF, Jung SM. Extraskeletal Ewing′s sarcoma of the parapharyngeal space. Br J Radiol 2004;77:1046-9.
- Cortez EA, Mattox DE, Holt GR, Gates GA. Unilateral tonsillar enlargement. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (1979) 1979;87:707-16.
- Shao CH, Huang SC, Hwang CF, Peng JP. Extraosseous Ewing sarcoma of the tonsil. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2012;41:E35-7.

| Figure 1:Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) scan of neck revealed well-defined homogenous soft-tissue mass 4 cm mass in tonsillar fossa extending into anterior tonsillar pillar and oropharyngeal wall (a); CECT scan of chest showed nodular lesions in right upper lobe of lung (b); biopsy of tonsil showing a sheet of regular, malignant round small undifferentiated cells with frequent mitoses (H and E, ×200) (c); tumor cells show diffuse membranous immunopositivity for mic-2. (H and E, ×400) while they are immunonegative for bcl-2 (inset) (d)
References
- Ng SH, Ko SF, Cheung YC, Wong HF, Jung SM. Extraskeletal Ewing′s sarcoma of the parapharyngeal space. Br J Radiol 2004;77:1046-9.
- Cortez EA, Mattox DE, Holt GR, Gates GA. Unilateral tonsillar enlargement. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (1979) 1979;87:707-16.
- Shao CH, Huang SC, Hwang CF, Peng JP. Extraosseous Ewing sarcoma of the tonsil. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2012;41:E35-7.


 PDF
PDF  Views
Views  Share
Share

