Neutropenia due to palbociclib: A word of caution?
CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 · Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 2016; 37(03): 206
DOI: DOI: 10.4103/0971-5851.190351

Publication History
Article published online:
12 July 2021
© 2016. Indian Society of Medical and Paediatric Oncology. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.)
Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A-12, 2nd Floor, Sector 2, Noida-201301 UP, India
Sir,
Palbociclib is an oral, selective, reversible inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6, which prevents cell cycle progression from G1 to S phase.[1] It was found to be beneficial in hormone-resistant advanced breast cancer when added to letrozole versus letrozole with placebo. Following this study (PALOMA-1), palbociclib got an accelerated approval, a way to rapidly review the clinical data (instead of a series of scheduled meetings) and faster marketing of drugs for such life-threatening diseases. In a subsequent phase 3 study (PALOMA-3), addition of palbociclib to fulvestrant in patients suffering from hormone-sensitive advanced breast cancer has also shown a survival benefit.[2]
Palbociclib has shown to cause a fair amount of severe neutropenia, resulting in significant interruptions and modifications of palbociclib [Table 1]. Neutropenia was associated with a very low incidence of febrile neutropenia in both these trials [Table 1] where patients in good general condition were carefully selected and monitored intensively. In actual clinical practice in the real world, the risk of infections during neutropenia due to palbociclib may increase and would warrant caution. Clinicians will certainly be afraid to prescribe it to endocrine-resistant, multiply relapsed, metastatic breast cancer patient with an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 2–3, the scene where exactly the current unmet need lies.
Table 1
Neutropenia with palbociclib
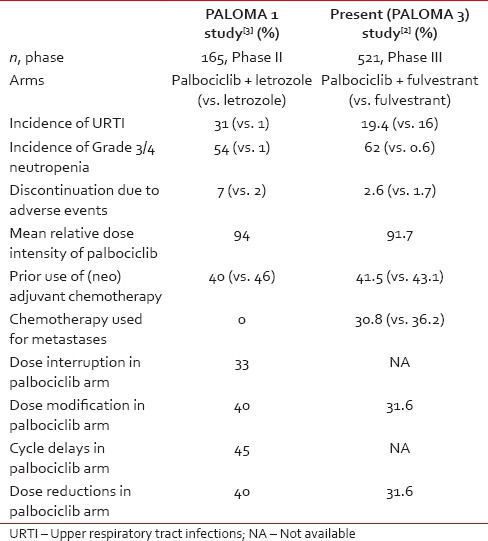
Whether this neutropenia is a class effect of this drug or due to dose and schedule effect is not known.
The recommended dose of palbociclib (125 mg/day orally for 3 weeks, followed by 1 week off) is derived from a very few phase, 1/2 studies resulting in limited information about tolerability.[3,4] Hence, to confirm its relationship with neutropenia, pharmacokinetic studies are needed in future and that should revisit the dosage and schedule of palbociclib.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.


 PDF
PDF  Views
Views  Share
Share

