Imaging Recommendations for Diagnosis, Staging and Management of Treatment-Related Complications in Cancer
CC BY 4.0 · Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 2023; 44(03): 322-333
DOI: DOI: 10.1055/s-0042-1760312
Abstract
Precision medicine is becoming increasingly common in oncology, with treatments tailored to individual patients and cancer. By integrating these underlying concepts of health care, chemotherapy and radiotherapy can be tailored to improve safety and efficacy. On the other hand, oncology treatment regimens may result in local and systemic changes and complications depending on the type of treatment. For the proper and prompt management of cancer patients, it is essential to interpret this posttreatment imaging correctly. This article aims at guiding treating physicians to be able to distinguish complications from expected posttreatment changes.
Publication History
Article published online:
01 March 2023
© 2023. The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A-12, 2nd Floor, Sector 2, Noida-201301 UP, India
Abstract
Precision medicine is becoming increasingly common in oncology, with treatments tailored to individual patients and cancer. By integrating these underlying concepts of health care, chemotherapy and radiotherapy can be tailored to improve safety and efficacy. On the other hand, oncology treatment regimens may result in local and systemic changes and complications depending on the type of treatment. For the proper and prompt management of cancer patients, it is essential to interpret this posttreatment imaging correctly. This article aims at guiding treating physicians to be able to distinguish complications from expected posttreatment changes.
Keywords
complications - oncology - radiology - reviewIntroduction
Precision medicine is becoming increasingly common in oncology, with treatments tailored to individual patients and cancer.[1] By integrating these underlying concepts of health care, chemotherapy and radiotherapy (RT) can be tailored to improve safety and efficacy.[2] On the other hand, oncology treatment regimens may result in local and systemic changes and complications depending on the type of treatment.[3] For the proper and prompt management of cancer patients, it is essential to interpret this posttreatment imaging correctly. This article aims at guiding treating physicians to be able to distinguish complications from expected posttreatment changes.
Etiopathogenesis and Risk Factors
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy impairs mucosal immunity. Stem cell transplantations and some chemotherapy agents result in neutropenia. These factors and other factors such as graft versus host disease, and the use of immunomodulatory agents increase the risk of infections in cancer patients during treatment.
Acute effects of RT are mainly on organs having rapid cell turnover, such as skin or mucosal surfaces. On the other hand, chronic or late complications of RT, such as fibrosis, perforation, or fistula formation, are a result of microvascular injury or direct parenchymal damage.[4]
Risk factors for treatment related complications are:
Local extent and histology of the primary neoplasm.
Preoperative chemotherapy and/or RT.
Type of radiation therapy.
Radiation dose, duration, and fractionation.
Size of the field of irradiation.
Concurrent use of chemotherapy.
Comorbid medical conditions.
Poor nutritional status.
Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation
Around 650,000 cancer patients receive systemic therapy or RT in the United States each year, while 180,000 receive both. The number of emergency department visits associated with cancer treatment outpaced visits related to overall health care. The most implicated cancers were lung (20.0%), breast (13.2%), and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (9.7%).
The most common complications in patients with hematologic malignancies were neutropenia (15.0%), sepsis (11.6%), and anemia (11.5%). In the case of solid tumor malignancies, the most frequent complications are sepsis (7.4%), neutropenia (7.3%), and anemia (6.7%).
Among the other common presentations, dehydration was among the most common complications associated with head and neck, colon, and esophageal cancers. Intestinal obstruction was commonly seen in gynecologic (ovary, uterus, and cervix) and gastrointestinal (GI) (colorectal and anal canal) cancers. GI hemorrhage was most commonly seen in prostate cancer. Congestive cardiac failure was commonly seen in breast cancer and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Pneumonia was associated with lung cancer and multiple myeloma while acute kidney injury (AKI) was most commonly associated with urinary bladder cancer.[5]
Imaging Referral Guidelines
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO), and American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) clinical guidelines are available for the management of immunotherapy-related toxicities[6] and cancer-related infections.[7] These guidelines have also mentioned the management of treatment-related complications according to symptoms.
No consensus guidelines exist on the frequency and modality of routine posttreatment imaging in the asymptomatic patient. In the case of signs and symptoms or the presence of worrisome features on clinical examinations, imaging protocol may be tailored to answer specific clinical questions.
Most of the literature on imaging of complications of cancer therapy predominantly uses computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
American College of Radiology (ACR) provided guidelines for the choice of imaging based on clinical presentation in the form of ACR appropriateness criteria. No specific guidelines are available on imaging of posttreatment complications in cancer.
National Cancer Grid (NCG) of India has formulated guidelines for palliative care of cancer but does not recommend imaging referral.[8] NCG, however, mentions the use of CT scans in cases where corrective measures are feasible and justifiable.[9]
Clinical/Diagnostic Workup (Other than Imaging)
Complications of systemic anticancer treatment are class-specific (i.e., agent-specific). A sepsis workup should be done if there is fever and/or cytopenia for localized or systemic features of inflammations (like intra-abdominal collection, pyelonephritis, etc.). Hypokalemia or paralytic ileus should be a differential diagnosis of intestinal obstruction. For suspected lung infection, sputum and blood culture sensitivity with Gram stain and/or bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) is helpful. Opportunistic and atypical infection should be ruled out by organism-specific polymerase chain reaction test from BAL and/or nasopharyngeal swab. Many tyrosine kinase inhibitors cause lung injury which is a diagnosis of exclusion sometimes with a classical clinical presentation with radiological findings. There is no specific diagnostic test other than a rapid response to steroid and drug withdrawal and infrequent reappearance on rechallenge.
For meningeal enhancement, cerebrospinal fluid cytology, cell count, biochemistry, and/or microbiological culture should be performed before labeling as carcinomatous meningitis in a clinical context. For immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-induced systemic complications, organ-specific diagnostic guidelines exist (NCCN, ESMO, and ASCO guidelines) and infection should be ruled out before giving high-dose steroids for immune-related adverse events (irAE). Blood-borne viral infection (i.e., hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human immunodeficiency virus) and Koch's should be ruled out before giving immunosuppressants like infliximab for the treatment of steroid-refractory irAE.
Imaging Guidelines
Screening
Currently, there is no evidence to support screening for complications that may develop as a result of treatment of cancers in the general population except for when they present with symptoms.
Diagnosis
Central Nervous System ([Table 1] and [2], [Fig. 1])
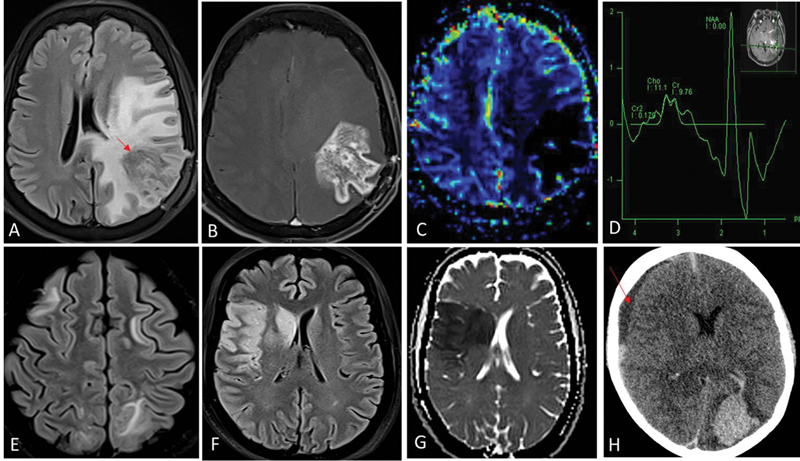
| Fig 1 :Radiation necrosis (A–D). One-year postradiation and temozolomide therapy for left temporal lobe glioblastoma. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) shows intermediate-hypointense signal areas (red arrow in A) in the left parietal lobe with surrounding disproportionate white matter edema. Contrast image (B) shows irregular and nodular enhancement (Swiss-cheese pattern) and relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) perfusion (C) did not show any increased perfusion. Presence of lipid-lactate peak in the corresponding area on magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy (D) represents necrosis. These imaging features are typical for radiation-induced injury. Absence of increased choline:NAA ratios (D) further helps exclude tumor progression. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) (E). Bilaterally asymmetrical FLAIR hyperintensity in frontoparietal white matter suggestive of vasogenic edema. Acute arterial infarcts (F and G). FLAIR hyperintense areas (F) in right frontoparietal cortex and right basal ganglia due to cytotoxic edema, showing restriction on the corresponding diffusion-weighted image (G) are suggestive of watershed territory infarcts. Intracerebral hematoma (H). Acute hematoma in left occipital lobe appears hyperdense on noncontrast computed tomography (CT). There is an intraventricular extension of bleed into the left lateral ventricle. Subdural hematoma is noted along right cerebral convexity as well (red arrow in H). Chemotherapeutic agents are common inciting factors for PRES, cerebral hematoma, and arterial infarcts.
|
CNS complication |
Symptoms |
Agents |
Diagnostic assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Acute and chronic encephalopathy |
Reduced attention, confusion, reduced alertness, hallucinations |
Ifosfamide, carmustine, cisplatin, cytarabine, fluorouracil, rituximab, alemtuzumab, brentuximab, blinatumomab |
MRI |
|
PRES |
Headache, confusion visual changes, and seizures |
Bevacizumab, ipilimumab, rituximab, sirolimus, sorafenib, sunitinib, tacrolimus, cisplatin, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, bortezomib, sorafenib, rituximab, tacrolimus |
MRI |
|
Hemorrhage |
Seizures, confusion, focal neurological deficits |
Bevacizumab, imatinib, TKIs, sirolimus, temsirolimus, everolimus, ridaforolimus |
CT or MRI |
|
Thromboembolic infarcts |
Focal neurological deficits |
Ipilimumab, bevacizumab, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, gemcitabine, bleomycin |
MRI (with DWI), cardiac assessment |
|
Venous sinus thrombosis |
Focal neurological deficits, seizures |
L-asparaginase |
MRI with MR venogram |
|
Cerebellar syndrome |
Dizziness, ataxia |
Cytarabine, capecitabine, bortezomib, rituximab, trastuzumab, cytosine arabinoside, 5-fluorouracil, and vincristine |
MRI |
|
Hypophysitis |
Fatigue and headache, hormonal imbalance |
Ipilimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, atezolizumab |
MRI |
|
Myasthenia gravis |
Fluctuating muscle weakness, ptosis, double vision, dysphagia, dysarthria, facial muscle weakness |
Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
No imaging |
|
Peripheral neuropathy |
Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
MRI brain or spine (exclude CVA, structural cause) |
|
|
Guillain–Barre syndrome |
Ascending, progressive muscle weakness, shortness of breath, facial weakness, numbness and tingling in the feet or hands, burning, stabbing, or shooting pain in affected areas, loss of balance, and coordination |
Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
No imaging |
|
Transverse myelitis |
Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
MRI brain and spine |
|
|
Encephalitis |
Confusion, altered mental status, altered behavior, headache, seizures, weakness, and gait instability |
Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
MRI |
|
Aseptic meningitis |
Headache, photophobia, neck stiffness, nausea or vomiting, and occasionally fever |
Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
MRI |
|
CNS complication |
Symptoms |
Diagnostic assessment |
|---|---|---|
|
Leukoencephalopathy |
Gait difficulties with frequent falls, cognitive impairment, and incontinence |
MRI |
|
Radiation Necrosis |
Headaches, short-term memory impairment, and focal seizures |
MRI with DWI, spectroscopy, and perfusion |
|
Cerebrovascular complications (infarcts, hemorrhage, SMART) |
Focal neurological deficits |
MR angiogram > CT angiogram |
|
Secondary CNS tumors |
Seizures, focal deficits, symptoms due to lobe involved |
MRI with contrast |
To establish the diagnosis of radiation (treatment)-related neurological complications, imaging is the first-line and most crucial investigation.[10] It also helps to rule out differential diagnosis such as metastases, tumor progression, hemorrhage, infarcts, and infections. MRI brain with intravenous contrast is the modality of choice. CT can be useful for quick assessment of raised intracranial tension, calcifications, acute hemorrhage, venous sinus thrombosis, or infarcts.
MRI angiogram with susceptibility-weighted imaging is preferred for evaluation of radiation-induced vascular injuries such as vascular narrowing or stenosis, capillary telangiectasia, cavernous malformations, microhemorrhages, and infarcts. CT can be useful for the detection of basal ganglia calcification associated with mineralizing microangiopathy.[11]
If patients with glioma are treated with RT and concurrent temozolomide after surgical resection, they become susceptible to radiation-related brain parenchymal damage, resulting in pseudoprogression and radiation necrosis.[12] The imaging modality of choice for radiation-related brain parenchymal injury is MRI with spectroscopy and perfusion. It helps to discriminate viable tumors from radiation necrosis/pseudoprogression.[13] Imaging guidelines are similar for radiation-induced necrosis associated with brain metastases following radiation therapy.[14] [15] [16]
MRI brain is the modality of choice for evaluation of chemotherapy-related neurotoxicity.[17] However, most drugs produce similar and nonspecific imaging patterns. The diagnosis can be established by resolution of MRI findings in post-drug cessation follow-up imaging. Few drugs have characteristic imaging findings and require additional MRI sequences to suggest the diagnosis. Areas of symmetrical diffusion restriction in white matter on diffusion-weighted imaging are most sensitive for detection of acute methotrexate toxicity post-intrathecal route of drug administration.[18] L-asparaginase cause venous sinus thrombosis which can be easily picked up on MRI with MR venography. Immunotherapeutic agents can cause autoimmune hypophysitis. MRI with pituitary sequences should be advised in this situation.
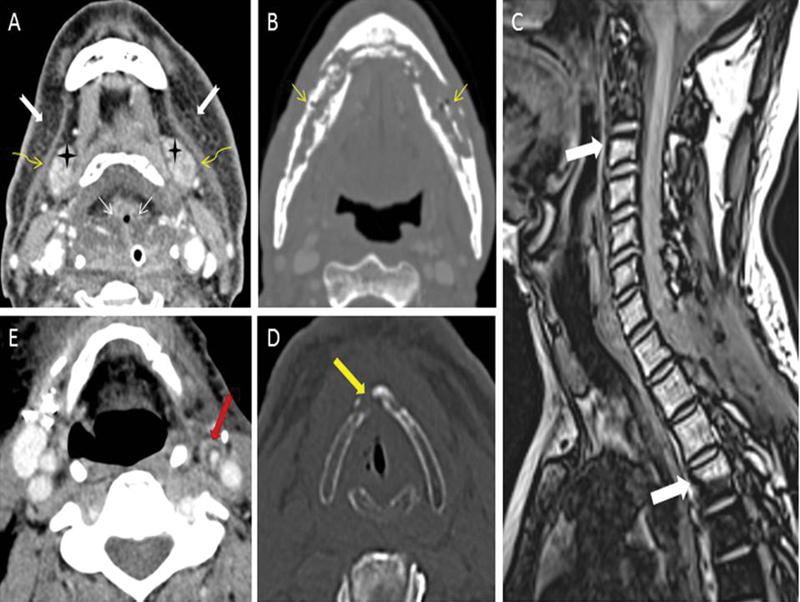
| Figure 2:(A) Expected radiotherapy (RT)-related soft tissue changes. Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) image in soft tissue window shows diffuse bilateral symmetrical subcutaneous fat reticulations (notched white arrows), thickened bilateral platysma muscles (curved yellow arrows), increased enhancement of bilateral submandibular glands (black stars), and edema of hypopharyngeal structure (thin straight white arrows). (B) Radiation-induced osteonecrosis. Axial contrast-enhanced CT image in bone window shows bizarre lysis, fragmentation, and sclerosis of the mandible (thin straight yellow arrows). Absence of expansile soft tissue at site of bone destruction rules out the possibility of recurrence. (C) Radiation-induced fatty marrow conversion. Sagittal Dixon T1-weighted fat magnetic resonance (MR) image shows conversion to fatty marrow from C3-D4 vertebrae with sharp margins at mid-C2 and mid-D4 levels (thick white arrows) corresponding with the radiation portal. (D) Radiation-induced chondronecrosis. Axial noncontrast-enhanced CT image in bone window kernel shows lysis of thyroid cartilage (thick yellow arrow) with air foci in the vicinity of the right vocal cord. (E) Radiation-induced atherosclerosis. Axial contrast-enhanced CT image in soft tissue window shows fatty atherosclerotic mural changes in the left external carotid artery (thick red arrow) causing luminal stenosis.
|
Complications |
Imaging recommendation of choice |
|---|---|
|
Radiation-induced brain necrosis |
MRI with IV contrast MR diffusion MR perfusion MR spectroscopy |
|
Brachial plexopathy |
MRI with or without IV contrast |
|
Spinal/Cranial nerve abnormality |
MRI with IV contrast CT with/without IV contrast |
|
Dental caries |
No imaging needed Clinical evaluation OPG (may be done) |
|
Trismus |
MRI T-M joints with or without IV contrast |
|
Radiation-induced lung injury/fibrosis |
HRCT thorax |
|
Radiation-induced bone and cartilage necrosis |
CT with IV contrast MRI with IV contrast |
|
Radiation-induced vascular changes |
CT angiogram Conventional angiogram |
|
Radiation-induced secondary neoplasms |
MRI with IV contrast CT with IV contrast |
|
Clinical presentation |
Complications |
Implicated therapy |
Imaging recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Dyspnea, cough, wheezing, and fever |
MIPI (medication-induced pulmonary injury) |
Cytotoxic chemotherapy TKI Immunotherapy |
CT (HRCT) scan without contrast |
|
Cough, low-grade fever, and dyspnea |
RILI (radiation-induced lung injury) |
Radiation therapy |
CT (HRCT) scan without contrast |
|
Implicated therapy |
Complication |
Imaging recommendation |
|---|---|---|
|
RT |
Coronary artery disease |
Coronary CT |
|
RT |
Valvular disease |
Echocardiography/coronary CT/cardiac MRI |
|
RT/Immunotherapy |
Pericarditis |
Echocardiography/coronary CT/cardiac MRI |
|
RT/ChT |
Cardiomyopathy |
Echocardiography/cardiac MRI |
|
ChT/Immunotherapy |
Myocarditis |
Echocardiography/cardiac MRI |
Certain cancer treatments can damage the heart and the cardiovascular system and cause congestive heart failure, ischemia, hypertension, hypotension, and arrhythmias.[26]
Currently, posttreatment cardiac evaluation is most often performed with echocardiography which is the first line of imaging.[27] Previous history of cancer and cancer therapy are associated with increased coronary artery calcium scores. These patients often undergo chest CT scan for oncologic surveillance. It is important to note the presence and degree of coronary artery calcifications during these routine scans. Coronary CT is the imaging of choice for coronary artery disease characterization.[28]
Late sequelae of high-dose chest RT can cause constrictive pericarditis and valve stenosis.
CT scan or MRI can be used for evaluation of these entities.
Cardiac MRI is the noninvasive gold standard for morpho-functional myocardial characterization, thereby improving the detection of cardiotoxicity over conventional functional assessment. Nevertheless, the routine use of cardiac MRI is not currently recommended.[27] [29]
Other Thoracic Organs
For evaluation of pleura, pericardium, thymus, great vessels, and lymph nodes both CT and MRI can be used. CT scan is the modality of choice and is used more frequently. MRI is used as a problem solving tool.[25]
Abdomen ([Table 6], [Fig. 3])
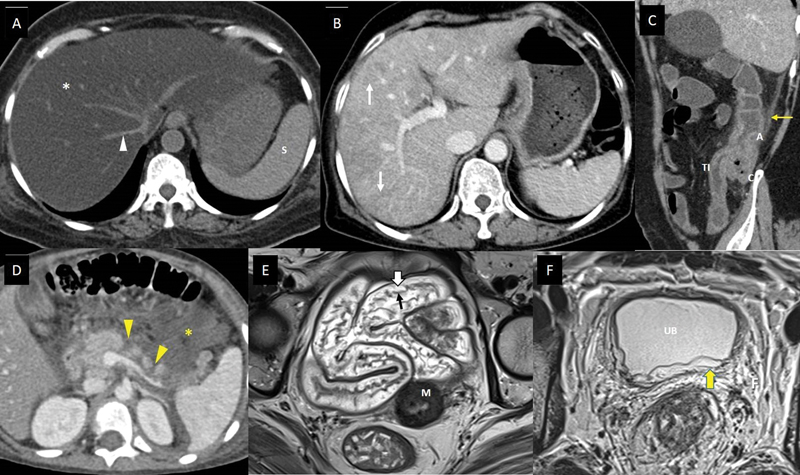
| Figure 3:Imaging features of abdominal complications of cancer therapy. (A) A 53-year-old suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukemia, on treatment with steroids and L-asparaginase, presented with mild abdominal pain and hyperbilirubinemia. Axial noncontrast computed tomography (CT) scan shows markedly reduced density of the entire hepatic parenchyma (white asterisk), suggesting fatty liver. The vessels (white arrowhead) and spleen (S) appear hyperdense to hepatic parenchyma in this noncontrast phase of CT scan due to diffuse fatty infiltration. (B) A 61-year-old lady with metastatic carcinoma stomach, on treatment with oxaliplatin. Axial CT scan of the abdomen with intravenous (IV) contrast done after few cycles of chemotherapy shows heterogeneous enhancement of the hepatic parenchyma with linear hypodensitites (white arrows), which is new compared to the baseline CT scan done 3 months back, suggesting oxaliplatin-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. (C) A 48-year-old man with lung adenocarcinoma, treated with pembrolizumab and carboplatin, presented to the emergency department (ED) complaining of abdominal pain, multiple episodes of diarrhea, and vomiting 6 days after a chemotherapy cycle. Sagittal CT scan of the abdomen with IV contrast shows thickened and edematous wall of ascending colon (A), caecum (C), and terminal ileum (TI), with surrounding fat stranding (yellow arrow), and maintained mural stratification. The patient was found to be severely neutropenic, and these imaging findings along with the clinical presentation, suggested neutropenic enterocolitis/typhlitis. (D) A 6-year-old boy suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukemia, on treatment regimen containing L-asparaginase, presented to the ED with acute abdominal pain and vomiting. He was found to be hypotensive and serum amylase and lipase were raised. Axial CT scan of the abdomen with IV contrast shows nonenhancing areas within the pancreatic parenchyma indicating necrosis (yellow arrowheads), and collection in peripancreatic region containing foci of fat (yellow asterisk). The features suggest acute necrotizing pancreatitis with peripancreatic fat necrosis. (E) A 47-year-old lady receiving radiation therapy for carcinoma of the cervix uteri, underwent response assessment magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) after 20 fractions along with cisplatin. Axial T2-weighted MR image shows submucosal edema as hyperintense signals (white block arrow) deep to the hypointense mucosal layer (black arrow), and maintained mural stratification, involving pelvic small bowel loops, indicating radiation-induced enteritis. The tumor with posttreatment changes is seen involving the cervix (M). (F) A 32-year-old man with rectal adenocarcinoma, underwent a response assessment MRI after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. He complained of mild lower urinary tract symptoms. Axial T2-weighted MR image shows edematous wall of urinary bladder (UB), with hyperintense signals involving the submucosa and muscularis (yellow block arrow), and surrounding edematous pelvic fat (F). The features suggested radiation-induced cystitis.
|
Clinical presentation |
Possible causes |
Implicated therapy |
Imaging recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Oral mucosal and gingival ulceration |
Mucositis (Therapy-related or Candida) |
Cytotoxic chemotherapy agents Allogeneic HSCT recipients with GVHD |
Usually no imaging recommended |
|
Retrosternal pain Dysphagia Odynophagia |
Esophagitis (due to mucositis or infective causes: Candida, HSV, bacterial, CMV, Aspergillus) Esophageal stricture/fibrosis/fistula |
Radiation therapy Cytotoxic chemotherapy agents Myelosuppressants (neutropenia, mucositis) |
Usually no imaging recommended (endoscopy needed) Fluoroscopy may be done, especially in chronic presentation CT scan with oral contrast: for fistula/stricture demonstration |
|
Upper abdominal pain, epigastric tenderness, vomiting |
Gastritis Gastric/duodenal ulcerations |
Radiation therapy |
Usually no imaging recommended (endoscopy needed) |
|
Upper abdominal pain, epigastric tenderness, vomiting, raised serum amylase, lipase |
Acute pancreatitis |
Cytarabine L-asparaginase ATRA Immunotherapy agents Gemcitabine Cytarabine |
CECT abdomen |
|
Incidental rise in serum amylase lipase |
− |
Sunitinib, sorafenib |
Usually no imaging recommended |
|
Acute abdominal pain (and tenderness) Fever Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea (sometimes bloody) |
Colitis/enterocolitis (neutropenic, Clostridioides difficile, GVHD, CMV, ischemic) Cholecystitis Appendicitis |
Myelosuppressants + Cytotoxic chemotherapy (esp. in acute leukemias, taxanes in solid tumors) (neutropenia, mucositis) |
CECT abdomen: for diagnosis, extent, complications (appendicitis, abscess, perforation) |
|
Perianal swelling, pain, erythema |
Anorectal cellulitis, fistula, abscess (usually polymicrobial: Enterobacteria, anaerobes, enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
Cytotoxic chemotherapy |
Consider CECT pelvis: for extent, drainable collections |
|
Diarrhea (acute) Malabsorption (chronic) |
Enteritis (therapy related or infective) |
Cytotoxic chemotherapy Radiation therapy (ileitis) |
Consider CECT/CT enterography in nonresolving or chronic cases |
|
Constipation with/without abdominal distension, vomiting |
Small/large bowel strictures, fistula, adhesions leading to acute/subacute obstruction Ileus |
Radiation therapy Vinca alkaloids |
Abdominal radiograph Fluoroscopy in subacute cases CECT abdomen |
|
Fever, burning micturition, hematuria, pyuria |
Urinary tract infections |
Myelosuppressants Genitourinary procedures/instrumentation |
Ultrasonography of urinary tract |
|
Rising urea, creatinine |
Renal failure (AKI: acute, CKD: chronic) |
Chemotherapy agents |
Ultrasonography of urinary tract MRI may be done for early detection of AKI |
|
Hematuria, frequency of micturition, burning micturition |
Hemorrhagic cystitis |
Cytotoxic agents (especially cyclophosphamide) Viral (in immunocompromised): BK virus, adenovirus, CMV Radiation therapy |
Cystoscopy in refractory cases For severe/doubtful cases: CT urogram/ MR urogram/USG urinary tract/retrograde pyelogram (if CT scan with IV contrast is contraindicated) |
|
Lower abdominal pain, distension in females Urinary incontinence Leakage of urine/stool through vagina |
Cervical stenosis Hematometra/pyometra Vesicovaginal fistula Rectovaginal/rectovesical fistula |
Radiation therapy (in pelvic cancers) |
Ultrasonography MRI pelvis/fistulogram CECT pelvis with delayed phase/rectal contrast |
|
Difficulty in micturition (usually males) |
Urethral stricture |
Radiation therapy |
Retrograde cystourethrography, voiding cystourethrography |
|
Females: amenorrhea, menstrual irregularities Males: features of hypogonadism, reduced sperm counts |
Gonadal dysfunction |
Cytotoxic chemotherapy Radiation therapy |
In addition to hormonal evaluation, ultrasonography of the pelvis/testes |
Liver injury symptoms include fatigue, right upper quadrant pain, nausea, vomiting, jaundice, abdominal swelling, and skin rashes. The different mechanisms of action of chemotherapy and RT may result in a broad spectrum of pathological and radiological hepatic injuries. These include acute or chronic hepatitis, steatosis, fibrosis, pseudocirrhosis, sinusoidal changes, and nodular hyperplasia. Ultrasonography (USG) is performed initially to rule out metastases, hemorrhage, and obstructive causes of jaundice. It may also detect ascites and gallbladder wall thickening (bystander effect). Either CT or MRI can be used for further characterization of liver involvement. MRI is more accurate in diagnosing steatosis/steatohepatitis, sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, and focal nodular hyperplasia-like nodules.[30] [31] [32]
For treatment-related oral mucosal and gingival ulceration, chemotherapy- and RT-induced nausea and vomiting (unless alternative causes are suspected, such as brain metastases or bowel obstruction), and uncomplicated mild diarrhea no imaging is needed.
For patients presenting with moderate or severe diarrhea, abdominopelvic CT scan with intravenous contrast needs to be done if complications such as enteritis, toxic megacolon, or abscess are suspected.[6] CT enterography may be performed in subacute or chronic situations.
Patients with suspected bowel obstruction (which may be due to complications of therapy such as stricture, adhesions, enteritis, and colitis) should undergo a supine abdominal radiograph as the initial investigation. Abdominopelvic CT scan with intravenous contrast would be needed to further localize and demonstrate the cause of obstruction. Subacute cases may be investigated with oral contrast fluoroscopy, small bowel follow-through or enema studies, CT, or MR enterography.
Patients with dysphagia, retrosternal pain, and odynophagia, that is, suspected esophagitis, endoscopy would be needed. Fluoroscopic examination (contrast swallow studies) may be done in subacute presentation. For suspected esophageal stricture, fibrosis, or fistula, fluoroscopy examination and/or CT scan with oral and intravenous contrast would be needed.
If a patient presents with upper abdominal pain, epigastric tenderness, and vomiting, radiation-induced gastritis or gastric/duodenal ulceration would be a possible cause, for which endoscopy would be diagnostic and no imaging would be required.
In case these symptoms are associated with raised serum amylase and lipase, acute pancreatitis is suspected, and an abdominopelvic CT scan with intravenous contrast is indicated. If the scan is normal, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography may be considered.
Neutropenic patients presenting with acute abdominal pain, fever, vomiting, and diarrhea, would be suspected to have infective or noninfective colitis/enterocolitis. USG would be recommended as an initial investigation and abdominopelvic CT scan with intravenous contrast would be indicated.
For patients with suspected urinary tract infection presenting with fever, burning micturition, hematuria, and/or pyuria, USG would be the initial imaging. Patients on cytotoxic chemotherapy (such as cyclophosphamide) or RT presenting with hematuria, hemorrhagic cystitis can be due to the therapy or viral infections. Cystoscopy and urinary tract imaging is indicated in refractory and severe cases. If renal function allows, CT urogram is done, otherwise, MR urogram and renal USG may be performed.[33] Patients with rising urea and creatinine would be suspected to have AKI or chronic kidney disease in appropriate setting. Usually, USG is performed. MRI may be done to evaluate the kidney and other organs.
If female patients on pelvic radiation therapy present with lower abdominal pain and distension, cervical stenosis with hematometra or pyometra is a possibility. USG would be the initial investigation of choice. MRI of the pelvis would demonstrate the cause better. Patients presenting with urinary incontinence, urine, or stool discharge through vagina would be suspected to have fistulas, and fluoroscopic examination with relevant contrast is the initial investigation. CT scan of the pelvis with intravenous contrast (delayed phase images) or with rectal contrast will delineate the communication better. MRI of the pelvis or MR fisulogram may demonstrate some fistulous communications better. In patients who present with difficulty in micturition following radiation therapy, urethral strictures are suspected and retrograde cystourethrography/voiding cystourethrography are required imaging modalities for diagnosis.
Bones and Soft Tissues ([Table 7])
|
Clinical presentation |
Imaging recommendation |
|---|---|
|
Back pain with or without radiculopathy[1] |
Radiograph of spine CT without IV contrast MRI without IV contrast |
|
New onset soft tissue swelling[2] |
Ultrasound of area of interest If nondiagnostic; CT or MRI of area of interest with IV contrast |
|
Osteonecrosis[3] |
MRI of area of interest without IV contrast CT of area of interest without IV contrast |
|
Vertebral compression fractures[4] |
MRI spine of area of interest without and with IV contrast |
|
Patients receiving estrogen therapy or ADT with increased risk for osteoporosis related fractures |
BMD measurement/DEXA every 2 years or more frequently depending upon age and risk factors[5] BMD measurement/DEXA and risk monitoring every 1- to 2-year interval[6] Baseline DEXA followed by DEXA scan at 1 year to assess risk and response[7] |
The imaging recommendations are given in [Table 7].[34] [35] [36]
Follow-Up and Surveillance
Women who were exposed to thoracic irradiation as an adolescent should undergo routine follow-up screening (with adjunctive breast MRI) sooner than usually recommended. Mammographic screening is recommended annually by the Society of Breast Imaging, ACR, and NCCN beginning 8 to 10 years after the radiation exposure.[37] [38]
For patients undergoing combined chemotherapy and radiation therapy, imaging monitoring of left ventricular ejection function has been recommended at 2-year intervals.[39] Echocardiography is typically used. In patients who are found to have decreased systolic function, the next step should be cardiac MRI.[40]
There exists no other substantial role for surveillance to detect treatment-related complications.
Principles of Management
Most of the grade 1or grade 2 systemic anticancer drug-related and RT toxicity is manageable with supportive care without altering the recommended dose and frequency. For any grade 3 or grade 4 toxicity every effort should be made to find out any identifiable underlying factor(s) contributing to such toxicity (like uncontrolled comorbidity, poor nutritional status, etc.). Any correctable cause should be addressed accordingly. Majority of the time dose reduction is recommended in case of grade 3/4 toxicity. Prophylactic hematopoietic growth factor should be used liberally whenever indicated to reduce the incidence of febrile neutropenia. Permanent interruption is required in majority of grade 4 and few grade 3 toxicities. Patient counseling, home remedies, early identification, and treatment of toxicities are very important and effective strategy to maintain treatment compliance. For ICI-induced irAE, well-recommended and well-studied organ-specific guidelines exist (ASCO and ESMO guidelines). No dose reduction is recommended or permitted for any ICI-related irAE. Initial antibiotics cover and ruling out underlying or associated infection is recommended for any immunosuppressive therapy to treat irAE. Imaging is required to differentiate treatment complications from infection and tumor recurrence.
Summary of Recommendations
There are no consensus guidelines regarding the frequency and modality of routine posttreatment imaging in an asymptomatic patient.
In the case of equivocal signs and symptoms or presence of worrisome features on clinical examinations and other laboratory tests, imaging protocol may be tailored to answer specific clinical questions.
Most imaging guidelines advocate the use of MRI and CT scan in complementary roles.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
References
- Badalamenti G, Messina C, De Luca I, Musso E, Casarin A, Incorvaia L. Soft tissue sarcomas in the precision medicine era: new advances in clinical practice and future perspectives. Radiol Med (Torino) 2019; 124 (04) 259-265
- Kucha N, Soni TP, Jakhotia N. et al. A prospective, comparative analysis of acute toxicity profile between three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT) and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) in locally advanced head and neck cancer patients. Cancer Treat Res Commun 2020; 25: 100223
- Ngo D, Jia JB, Green CS, Gulati AT, Lall C. Cancer therapy related complications in the liver, pancreas, and biliary system: an imaging perspective. Insights Imaging 2015; 6 (06) 665-677
- Stone JB, DeAngelis LM. Cancer-treatment-induced neurotoxicity–focus on newer treatments. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2016; 13 (02) 92-105
- Jairam V, Lee V, Park HS. et al. Treatment-related complications of systemic therapy and radiotherapy. JAMA Oncol 2019; 5 (07) 1028-1035
- Thompson JA, Schneider BJ, Brahmer J. et al. Management of Immunotherapy-Related Toxicities, Version 1.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2022; 20 (04) 387-405 DOI: 10.6004/jnccn.2022.0020.
- Baden LR, Swaminathan S, Angarone M. et al. Prevention and Treatment of Cancer-Related Infections, Version 2.2016, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2016; 14 (07) 882-913 DOI: 10.6004/jnccn.2016.0093.
- NCG palliative care guidelines 2021 [Internet]. NCG; 2021. . Accessed April 1, 2022, at: https://tmc.gov.in/ncg/index.php/guidelines/palliative-care-guidelines
- NCG. Approach to managing malignant bowel obstruction [Internet]. NCG Guidelines for palliative care. 2021 . Accessed April 1, 2022, at: https://tmc.gov.in/ncg/images/Approach%-20to%-20managing%-20Malignant%-20Bowel%-20Obstruction.pdf
- Kanda T, Wakabayashi Y, Zeng F. et al. Imaging findings in radiation therapy complications of the central nervous system. Jpn J Radiol 2018; 36 (09) 519-527
- Albano D, Benenati M, Bruno A. et al; Young SIRM Working Group. Imaging side effects and complications of chemotherapy and radiation therapy: a pictorial review from head to toe. Insights Imaging 2021; 12 (01) 76
- Kessler AT, Bhatt AA. Brain tumour post-treatment imaging and treatment-related complications. Insights Imaging 2018; 9 (06) 1057-1075
- Shah R, Vattoth S, Jacob R. et al. Radiation necrosis in the brain: imaging features and differentiation from tumor recurrence. Radiographics 2012; 32 (05) 1343-1359
- Leao DJ, Craig PG, Godoy LF, Leite CC, Policeni B. Response assessment in neuro-oncology criteria for gliomas: practical approach using conventional and advanced techniques. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2020; 41 (01) 10-20
- Chukwueke UN, Wen PY. Use of the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria in clinical trials and clinical practice. CNS Oncol 2019; 8 (01) CNS28
- Linhares P, Carvalho B, Figueiredo R, Reis RM, Vaz R. Early pseudoprogression following chemoradiotherapy in glioblastoma patients: the value of RANO evaluation. J Oncol 2013; 2013: 690585
- Dietrich J, Klein JP. Imaging of cancer therapy–induced central nervous system toxicity. Neurol Clin [Internet]. 2014. Accessed December 13, 2022, at: https://www.neurologic.theclinics.com/article/S0733-8619(13)00087-X/abstract
- Sindhwani G, Arora M, Thakker VD, Jain A. MRI in chemotherapy induced leukoencephalopathy: report of two cases and radiologist's perspective. J Clin Diagn Res 2017; 11 (07) TD08-TD09
- Glastonbury CM, Parker EE, Hoang JK. The postradiation neck: evaluating response to treatment and recognizing complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2010; 195 (02) W164-71
- Gehani A, Sen S, Chatterjee S, Mukhopadhyay S. Imaging features of postradiotherapy changes in head and neck cancers. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2021; 31 (03) 661-669
- Nishino M, Ramaiya NH, Awad MM. et al. PD-1 inhibitor-related pneumonitis in advanced cancer patients: radiographic patterns and clinical course. Clin Cancer Res 2016; 22 (24) 6051-6060
- Terbuch A, Tiu C, Candilejo IM. et al. Radiological patterns of drug-induced interstitial lung disease (DILD) in early-phase oncology clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res 2020; 26 (18) 4805-4813
- Weber JS, Kähler KC, Hauschild A. Management of immune-related adverse events and kinetics of response with ipilimumab. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30 (21) 2691-2697
- Lee H, Lee HY, Sun J-M. et al. Transient asymptomatic pulmonary opacities during osimertinib treatment and its clinical implication. J Thorac Oncol 2018; 13 (08) 1106-1112
- Benveniste MF, Gomez D, Carter BW. et al. Recognizing radiation therapy-related complications in the chest. Radiographics 2019; 39 (02) 344-366
- Yeh ETH, Tong AT, Lenihan DJ. et al. Cardiovascular complications of cancer therapy: diagnosis, pathogenesis, and management. Circulation 2004; 109 (25) 3122-3131
- Čelutkienė J, Pudil R, López-Fernández T. et al. Role of cardiovascular imaging in cancer patients receiving cardiotoxic therapies: a position statement on behalf of the Heart Failure Association (HFA), the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) and the Cardio-Oncology Council of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur J Heart Fail 2020; 22 (09) 1504-1524
- Whitlock MC, Yeboah J, Burke GL, Chen H, Klepin HD, Hundley WG. Cancer and its association with the development of coronary artery calcification: an assessment from the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. J Am Heart Assoc 2015; 4 (11) e002533
- Wang DY, Salem J-E, Cohen JV. et al. Fatal toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 2018; 4 (12) 1721-1728
- Gatti M, Calandri M, Bergamasco L. et al. Characterization of the arterial enhancement pattern of focal liver lesions by multiple arterial phase magnetic resonance imaging: comparison between hepatocellular carcinoma and focal nodular hyperplasia. Radiol Med (Torino) 2020; 125 (04) 348-355
- Vernuccio F, Godfrey D, Meyer M. et al. Local tumor control and patient outcome using stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: iRECIST as a potential substitute for traditional criteria. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2019; 213 (06) 1232-1239
- Hennedige TP, Hallinan JTPD, Leung FP. et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance elastography and diffusion-weighted imaging for differentiating benign and malignant liver lesions. Eur Radiol 2016; 26 (02) 398-406
- UpToDate [Internet]. Accessed April 1, 2022, at: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/chemotherapy-and-radiation-related-hemorrhagic-cystitis-in-cancer-patients
- Hutchins TA, Peckham M, Shah LM. et al; Expert Panel on Neurological Imaging. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® low back pain: 2021 update. J Am Coll Radiol 2021; 18 (11S, Supplement): S361-S379
- Kransdorf MJ, Murphey MD, Wessell DE. et al; Expert Panel on Musculoskeletal Imaging. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® soft-tissue masses. J Am Coll Radiol 2018; 15 (5S): S189-S197
- Shah LM, Jennings JW, Kirsch CFE. et al; Expert Panels on Neurological Imaging, Interventional Radiology, and Musculoskeletal Imaging. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® management of vertebral compression fractures. J Am Coll Radiol 2018; 15 (11S): S347-S364
- Lee CH, Dershaw DD, Kopans D. et al. Breast cancer screening with imaging: recommendations from the Society of Breast Imaging and the ACR on the use of mammography, breast MRI, breast ultrasound, and other technologies for the detection of clinically occult breast cancer. J Am Coll Radiol 2010; 7 (01) 18-27
- Bevers TB, Anderson BO, Bonaccio E. et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer screening and diagnosis. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2009; 7 (10) 1060-1096
- Johnson CB, Sulpher J, Stadnick E. Evaluation, prevention and management of cancer therapy-induced cardiotoxicity: a contemporary approach for clinicians. Curr Opin Cardiol 2015; 30 (02) 197-204
- Huang H, Nijjar PS, Misialek JR. et al. Accuracy of left ventricular ejection fraction by contemporary multiple gated acquisition scanning in patients with cancer: comparison with cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2017; 19 (01) 34
Address for correspondence
Sumit Mukhopadhyay, MDDepartment of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Tata Medical CenterKolkata, West Bengal 700160IndiaPublication History
Article published online:
01 March 2023© 2023. The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A-12, 2nd Floor, Sector 2, Noida-201301 UP, India

| Fig 1 :Radiation necrosis (A–D). One-year postradiation and temozolomide therapy for left temporal lobe glioblastoma. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) shows intermediate-hypointense signal areas (red arrow in A) in the left parietal lobe with surrounding disproportionate white matter edema. Contrast image (B) shows irregular and nodular enhancement (Swiss-cheese pattern) and relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) perfusion (C) did not show any increased perfusion. Presence of lipid-lactate peak in the corresponding area on magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy (D) represents necrosis. These imaging features are typical for radiation-induced injury. Absence of increased choline:NAA ratios (D) further helps exclude tumor progression. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) (E). Bilaterally asymmetrical FLAIR hyperintensity in frontoparietal white matter suggestive of vasogenic edema. Acute arterial infarcts (F and G). FLAIR hyperintense areas (F) in right frontoparietal cortex and right basal ganglia due to cytotoxic edema, showing restriction on the corresponding diffusion-weighted image (G) are suggestive of watershed territory infarcts. Intracerebral hematoma (H). Acute hematoma in left occipital lobe appears hyperdense on noncontrast computed tomography (CT). There is an intraventricular extension of bleed into the left lateral ventricle. Subdural hematoma is noted along right cerebral convexity as well (red arrow in H). Chemotherapeutic agents are common inciting factors for PRES, cerebral hematoma, and arterial infarcts.

| Figure 2:(A) Expected radiotherapy (RT)-related soft tissue changes. Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) image in soft tissue window shows diffuse bilateral symmetrical subcutaneous fat reticulations (notched white arrows), thickened bilateral platysma muscles (curved yellow arrows), increased enhancement of bilateral submandibular glands (black stars), and edema of hypopharyngeal structure (thin straight white arrows). (B) Radiation-induced osteonecrosis. Axial contrast-enhanced CT image in bone window shows bizarre lysis, fragmentation, and sclerosis of the mandible (thin straight yellow arrows). Absence of expansile soft tissue at site of bone destruction rules out the possibility of recurrence. (C) Radiation-induced fatty marrow conversion. Sagittal Dixon T1-weighted fat magnetic resonance (MR) image shows conversion to fatty marrow from C3-D4 vertebrae with sharp margins at mid-C2 and mid-D4 levels (thick white arrows) corresponding with the radiation portal. (D) Radiation-induced chondronecrosis. Axial noncontrast-enhanced CT image in bone window kernel shows lysis of thyroid cartilage (thick yellow arrow) with air foci in the vicinity of the right vocal cord. (E) Radiation-induced atherosclerosis. Axial contrast-enhanced CT image in soft tissue window shows fatty atherosclerotic mural changes in the left external carotid artery (thick red arrow) causing luminal stenosis.

| Figure 3:Imaging features of abdominal complications of cancer therapy. (A) A 53-year-old suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukemia, on treatment with steroids and L-asparaginase, presented with mild abdominal pain and hyperbilirubinemia. Axial noncontrast computed tomography (CT) scan shows markedly reduced density of the entire hepatic parenchyma (white asterisk), suggesting fatty liver. The vessels (white arrowhead) and spleen (S) appear hyperdense to hepatic parenchyma in this noncontrast phase of CT scan due to diffuse fatty infiltration. (B) A 61-year-old lady with metastatic carcinoma stomach, on treatment with oxaliplatin. Axial CT scan of the abdomen with intravenous (IV) contrast done after few cycles of chemotherapy shows heterogeneous enhancement of the hepatic parenchyma with linear hypodensitites (white arrows), which is new compared to the baseline CT scan done 3 months back, suggesting oxaliplatin-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. (C) A 48-year-old man with lung adenocarcinoma, treated with pembrolizumab and carboplatin, presented to the emergency department (ED) complaining of abdominal pain, multiple episodes of diarrhea, and vomiting 6 days after a chemotherapy cycle. Sagittal CT scan of the abdomen with IV contrast shows thickened and edematous wall of ascending colon (A), caecum (C), and terminal ileum (TI), with surrounding fat stranding (yellow arrow), and maintained mural stratification. The patient was found to be severely neutropenic, and these imaging findings along with the clinical presentation, suggested neutropenic enterocolitis/typhlitis. (D) A 6-year-old boy suffering from acute lymphoblastic leukemia, on treatment regimen containing L-asparaginase, presented to the ED with acute abdominal pain and vomiting. He was found to be hypotensive and serum amylase and lipase were raised. Axial CT scan of the abdomen with IV contrast shows nonenhancing areas within the pancreatic parenchyma indicating necrosis (yellow arrowheads), and collection in peripancreatic region containing foci of fat (yellow asterisk). The features suggest acute necrotizing pancreatitis with peripancreatic fat necrosis. (E) A 47-year-old lady receiving radiation therapy for carcinoma of the cervix uteri, underwent response assessment magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) after 20 fractions along with cisplatin. Axial T2-weighted MR image shows submucosal edema as hyperintense signals (white block arrow) deep to the hypointense mucosal layer (black arrow), and maintained mural stratification, involving pelvic small bowel loops, indicating radiation-induced enteritis. The tumor with posttreatment changes is seen involving the cervix (M). (F) A 32-year-old man with rectal adenocarcinoma, underwent a response assessment MRI after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. He complained of mild lower urinary tract symptoms. Axial T2-weighted MR image shows edematous wall of urinary bladder (UB), with hyperintense signals involving the submucosa and muscularis (yellow block arrow), and surrounding edematous pelvic fat (F). The features suggested radiation-induced cystitis.
References
- Badalamenti G, Messina C, De Luca I, Musso E, Casarin A, Incorvaia L. Soft tissue sarcomas in the precision medicine era: new advances in clinical practice and future perspectives. Radiol Med (Torino) 2019; 124 (04) 259-265
- Kucha N, Soni TP, Jakhotia N. et al. A prospective, comparative analysis of acute toxicity profile between three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT) and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) in locally advanced head and neck cancer patients. Cancer Treat Res Commun 2020; 25: 100223
- Ngo D, Jia JB, Green CS, Gulati AT, Lall C. Cancer therapy related complications in the liver, pancreas, and biliary system: an imaging perspective. Insights Imaging 2015; 6 (06) 665-677
- Stone JB, DeAngelis LM. Cancer-treatment-induced neurotoxicity–focus on newer treatments. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2016; 13 (02) 92-105
- Jairam V, Lee V, Park HS. et al. Treatment-related complications of systemic therapy and radiotherapy. JAMA Oncol 2019; 5 (07) 1028-1035
- Thompson JA, Schneider BJ, Brahmer J. et al. Management of Immunotherapy-Related Toxicities, Version 1.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2022; 20 (04) 387-405 DOI: 10.6004/jnccn.2022.0020.
- Baden LR, Swaminathan S, Angarone M. et al. Prevention and Treatment of Cancer-Related Infections, Version 2.2016, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2016; 14 (07) 882-913 DOI: 10.6004/jnccn.2016.0093.
- NCG palliative care guidelines 2021 [Internet]. NCG; 2021. . Accessed April 1, 2022, at: https://tmc.gov.in/ncg/index.php/guidelines/palliative-care-guidelines
- NCG. Approach to managing malignant bowel obstruction [Internet]. NCG Guidelines for palliative care. 2021 . Accessed April 1, 2022, at: https://tmc.gov.in/ncg/images/Approach to managing Malignant Bowel Obstruction.pdf
- Kanda T, Wakabayashi Y, Zeng F. et al. Imaging findings in radiation therapy complications of the central nervous system. Jpn J Radiol 2018; 36 (09) 519-527
- Albano D, Benenati M, Bruno A. et al; Young SIRM Working Group. Imaging side effects and complications of chemotherapy and radiation therapy: a pictorial review from head to toe. Insights Imaging 2021; 12 (01) 76
- Kessler AT, Bhatt AA. Brain tumour post-treatment imaging and treatment-related complications. Insights Imaging 2018; 9 (06) 1057-1075
- Shah R, Vattoth S, Jacob R. et al. Radiation necrosis in the brain: imaging features and differentiation from tumor recurrence. Radiographics 2012; 32 (05) 1343-1359
- Leao DJ, Craig PG, Godoy LF, Leite CC, Policeni B. Response assessment in neuro-oncology criteria for gliomas: practical approach using conventional and advanced techniques. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2020; 41 (01) 10-20
- Chukwueke UN, Wen PY. Use of the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria in clinical trials and clinical practice. CNS Oncol 2019; 8 (01) CNS28
- Linhares P, Carvalho B, Figueiredo R, Reis RM, Vaz R. Early pseudoprogression following chemoradiotherapy in glioblastoma patients: the value of RANO evaluation. J Oncol 2013; 2013: 690585
- Dietrich J, Klein JP. Imaging of cancer therapy–induced central nervous system toxicity. Neurol Clin [Internet]. 2014. Accessed December 13, 2022, at: https://www.neurologic.theclinics.com/article/S0733-8619(13)00087-X/abstract
- Sindhwani G, Arora M, Thakker VD, Jain A. MRI in chemotherapy induced leukoencephalopathy: report of two cases and radiologist's perspective. J Clin Diagn Res 2017; 11 (07) TD08-TD09
- Glastonbury CM, Parker EE, Hoang JK. The postradiation neck: evaluating response to treatment and recognizing complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2010; 195 (02) W164-71
- Gehani A, Sen S, Chatterjee S, Mukhopadhyay S. Imaging features of postradiotherapy changes in head and neck cancers. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2021; 31 (03) 661-669
- Nishino M, Ramaiya NH, Awad MM. et al. PD-1 inhibitor-related pneumonitis in advanced cancer patients: radiographic patterns and clinical course. Clin Cancer Res 2016; 22 (24) 6051-6060
- Terbuch A, Tiu C, Candilejo IM. et al. Radiological patterns of drug-induced interstitial lung disease (DILD) in early-phase oncology clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res 2020; 26 (18) 4805-4813
- Weber JS, Kähler KC, Hauschild A. Management of immune-related adverse events and kinetics of response with ipilimumab. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30 (21) 2691-2697
- Lee H, Lee HY, Sun J-M. et al. Transient asymptomatic pulmonary opacities during osimertinib treatment and its clinical implication. J Thorac Oncol 2018; 13 (08) 1106-1112
- Benveniste MF, Gomez D, Carter BW. et al. Recognizing radiation therapy-related complications in the chest. Radiographics 2019; 39 (02) 344-366
- Yeh ETH, Tong AT, Lenihan DJ. et al. Cardiovascular complications of cancer therapy: diagnosis, pathogenesis, and management. Circulation 2004; 109 (25) 3122-3131
- Čelutkienė J, Pudil R, López-Fernández T. et al. Role of cardiovascular imaging in cancer patients receiving cardiotoxic therapies: a position statement on behalf of the Heart Failure Association (HFA), the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) and the Cardio-Oncology Council of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur J Heart Fail 2020; 22 (09) 1504-1524
- Whitlock MC, Yeboah J, Burke GL, Chen H, Klepin HD, Hundley WG. Cancer and its association with the development of coronary artery calcification: an assessment from the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. J Am Heart Assoc 2015; 4 (11) e002533
- Wang DY, Salem J-E, Cohen JV. et al. Fatal toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 2018; 4 (12) 1721-1728
- Gatti M, Calandri M, Bergamasco L. et al. Characterization of the arterial enhancement pattern of focal liver lesions by multiple arterial phase magnetic resonance imaging: comparison between hepatocellular carcinoma and focal nodular hyperplasia. Radiol Med (Torino) 2020; 125 (04) 348-355
- Vernuccio F, Godfrey D, Meyer M. et al. Local tumor control and patient outcome using stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: iRECIST as a potential substitute for traditional criteria. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2019; 213 (06) 1232-1239
- Hennedige TP, Hallinan JTPD, Leung FP. et al. Comparison of magnetic resonance elastography and diffusion-weighted imaging for differentiating benign and malignant liver lesions. Eur Radiol 2016; 26 (02) 398-406
- UpToDate [Internet]. Accessed April 1, 2022, at: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/chemotherapy-and-radiation-related-hemorrhagic-cystitis-in-cancer-patients
- Hutchins TA, Peckham M, Shah LM. et al; Expert Panel on Neurological Imaging. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® low back pain: 2021 update. J Am Coll Radiol 2021; 18 (11S, Supplement): S361-S379
- Kransdorf MJ, Murphey MD, Wessell DE. et al; Expert Panel on Musculoskeletal Imaging. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® soft-tissue masses. J Am Coll Radiol 2018; 15 (5S): S189-S197
- Shah LM, Jennings JW, Kirsch CFE. et al; Expert Panels on Neurological Imaging, Interventional Radiology, and Musculoskeletal Imaging. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® management of vertebral compression fractures. J Am Coll Radiol 2018; 15 (11S): S347-S364
- Lee CH, Dershaw DD, Kopans D. et al. Breast cancer screening with imaging: recommendations from the Society of Breast Imaging and the ACR on the use of mammography, breast MRI, breast ultrasound, and other technologies for the detection of clinically occult breast cancer. J Am Coll Radiol 2010; 7 (01) 18-27
- Bevers TB, Anderson BO, Bonaccio E. et al; National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: breast cancer screening and diagnosis. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2009; 7 (10) 1060-1096
- Johnson CB, Sulpher J, Stadnick E. Evaluation, prevention and management of cancer therapy-induced cardiotoxicity: a contemporary approach for clinicians. Curr Opin Cardiol 2015; 30 (02) 197-204
- Huang H, Nijjar PS, Misialek JR. et al. Accuracy of left ventricular ejection fraction by contemporary multiple gated acquisition scanning in patients with cancer: comparison with cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2017; 19 (01) 34


 PDF
PDF  Views
Views  Share
Share

