Benson’s Relaxation Effect in Comparing to Systematic Desensitization on Anxiety of Female Nurses: A Randomized Clinical Trial
CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 · Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol 2017; 38(02): 111-115
DOI: DOI: 10.4103/ijmpo.ijmpo_183_16
Abstract
Introduction: Nursing staffs expose to a high level of anxiety. This study aimed to compare the effect of Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization methods for decreasing the anxiety score of nurses. Materials and Methods: In a randomized clinical trial, 72 female nurses were assigned randomly to three different groups. Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization were used as intervention beside control group. After intervention, the Spielberger state-trait anxiety inventory was used for measuring the anxiety score. Analysis of variance (ANOVA), Tukey test, and paired t-test were applied for comparing three group scores. Results: The ANOVA test showed that a significant difference among three groups regarding scores of posttrait and poststate anxiety (P < 0 class="b" xss=removed>Conclusion: Both Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization methods are effective in improvement of the state and trait dimensions of anxiety. However, these methods could be applied in stressful situation among medical staffs of students.
Keywords
Anxiety - Benson's relaxation - nurse - Spielberger scale - stress - systematic desensitizationPublication History
Article published online:
06 July 2021
© 2017. Indian Society of Medical and Paediatric Oncology. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.)
Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
A-12, 2nd Floor, Sector 2, Noida-201301 UP, India
Abstract
Introduction:
Nursing staffs expose to a high level of anxiety. This study aimed to compare the effect of Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization methods for decreasing the anxiety score of nurses.
Materials and Methods:
In a randomized clinical trial, 72 female nurses were assigned randomly to three different groups. Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization were used as intervention beside control group. After intervention, the Spielberger state-trait anxiety inventory was used for measuring the anxiety score. Analysis of variance (ANOVA), Tukey test, and paired t-test were applied for comparing three group scores.
Results:
The ANOVA test showed that a significant difference among three groups regarding scores of posttrait and poststate anxiety (P < 0>
Conclusion:
Both Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization methods are effective in improvement of the state and trait dimensions of anxiety. However, these methods could be applied in stressful situation among medical staffs of students.
Introduction
Psychological stress and anxiety are the most important unfortunate consequence of medical jobs, especially in nursing for coursework, clinical experiences, and personal issues.[1,2] Nursing staffs expose to a high level of anxiety and stress that can cause a nurse experience fear about poor performance and embarrassment due to inadequate staffing, changes in the working place, and lack of administrative support.[1,3] Moreover, caring to patients caused a synergism effect on the nurses’ anxiety due to emotional challenges of working with the sick increased acuity of patients and patients’ demands.[1,4,5,6] Moreover, shifting job beside the high load of work effects on the physical and psychological aspect of medical staffs such as nurses.[7,8,9]
Anxiety is the most psychological disorder and the most common response to the stressful condition that could cause the uncontrolled reactions including physical and emotional behaviors. The anxiety is effective on the quality of care in the nurses in clinical place works.[10,11] There were medical and nonmedical treatments for muscular relaxation and improvement of anxiety.[12,13,14,15] In recent studies, some stress management approaches are assessed in nursing or in the patients for control or improvements of stress or anxiety.[1,16,17,18,19] Some of these relaxation therapy techniques such as applied relaxation, relaxation and imagery, relaxation response mediation, emotional freedom technique, and the combination of relaxation techniques and back massage are used and showed improvement in the quality of life and decrease in pain, anxiety, and stress in patients and staffs.[1,17] Moreover, the effect of Benson's relaxation technique is assessed in patients for decreasing the pain, stress, and anxiety or for increasing the sleep quality.[20,21]
Benson's relaxation is one of the best muscular relaxations that effective on the pulse rate, respiratory function, and heart workload.[14] Benson's technique works by the alignment of hypothalamus and decreasing the sympathetic and parasympathetic practices. Moreover, systematic desensitization was beneficial in decreasing the psychological stress.[22] However, the effect of both Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization techniques is not assessed for decreasing of nurse's anxiety based on our search. Therefore, the current study aimed to compare the effectiveness of two intervention including Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization methods for decreasing the anxiety score of nurses against the control group in a randomized clinical trial.
Materials and Methods
In a randomized clinical trial, 110 female nurses recruited in Borujerd, Iran, at 2015. First, informed consent was taken from all eligible individuals, and the Ethical Committee of Arak University of Medical Sciences approved the study protocol. Moreover, this study is registered in the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials. The primary data including demographic characteristics such as age, gender, education, marital status, job history, and the employee status were obtained. Then, the status of anxiety of individuals determined and who have the anxiety score higher than 43 included in the study. Individuals who did not affect to anxiety based on the Spielberger anxiety scale and who did not consent for participating in the study were excluded from the study. Therefore, 72 female nurses of 84 who have the anxiety score higher than 43 were assigned randomly into three different groups.
The sample size calculated based on the standard deviation and acceptable power and alpha error. According to sample size calculation, 24 individuals should be assess in each group. For the first group, Benson's relaxation method was applied, and for the second group, systematic desensitization was used. In Benson's relaxation group, the guideline of muscular relaxation heard by headphone and fulfilled for three sessions and each session continued for 20 min. Moreover, in systematic desensitization group, a skilled, trained therapist the participants’ nurses for three sessions and 20 min in each session. Third group was the control. The anxiety score measured among the individuals of three groups at the baseline and 1 month after the study inception.
Spielberger state-trait anxiety inventory (STAI) was used for measurement the anxiety score in both intervention and control groups. This questionnaire measured the two important dimensions of anxiety including state anxiety and trait anxiety. The state anxiety scale measures the emotions of the individuals in the snapshot time as time of responding to the questionnaire. Moreover, the trait anxiety scale evaluates the general emotions of individuals.[23,24] The STAI scale include forty items comprising twenty items measuring the state anxiety and twenty other items measuring trait anxiety. Each item score varied between 1 and 4 and the total score of each dimension of Spielberger questionnaire changes from 20 to 80. The higher score shows more anxiety of the individuals. The anxiety was defined as the Spielberger questionnaire calculated for a individual higher than 43. A score of <43 href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5582545/#ref25" rid="ref25" class=" bibr popnode" role="button" aria-expanded="false" aria-haspopup="true" xss=removed>25]
Data analysis
Mean and standard deviation were used for description of data and variables. The normality of the anxiety scores had assessed by Kolmogorov–Smirnov test in each group. Based on normality results of the dependent variables among three studied groups, parametric test was used. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied for comparing the anxiety score among three groups and Tukey test was used for post hoc test. Paired t-test utilized for assessing the statistical difference between baseline measurements and final scores in each group. All the statistical analysis was conducted in SPSS software (Version 18.0. Chicago, USA: SPSS Inc.).
Results
The mean age of participants was 34.5 ± 5.3 years and varied since 25–51 years. The mean of job history was 5.12 ± 3.04 years. The results in Table 1 show the baseline measurements analysis. Based on the results, there was no significant difference among three studied groups regarding the age of participants, job history, and pretrait and prestate anxiety scores. In addition, the education level was no significant in three groups (P = 0.594). Therefore, the randomization method was adequate for random allocation of recruited individuals in three groups.
Table 1
The baseline measurements analysis in three studied groups including systematic desensitization, Benson's relaxation, and control
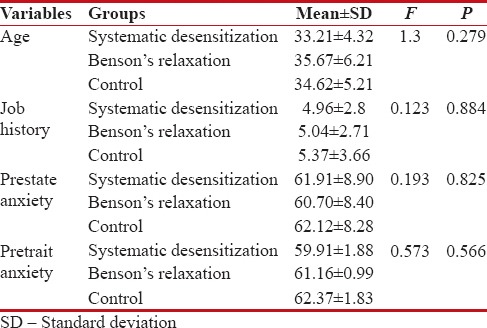
|
The ANOVA was conducted to compare the posttrait and poststate anxiety among three groups [Table 2]. The F-test showed that a significant difference among three groups regarding scores of posttrait and poststate anxiety (P < 0 xss=removed>P < 0 xss=removed>post hoc test was used to compare groups one by one, and the results showed that Benson's relaxation method was similar to systematic desensitization method in decreasing the trait and state anxiety score (P = 0.903). Therefore, both Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization intervention methods were effective in decreasing of the anxiety score of nurses. However, the effect of systematic desensitization was more than Benson's relaxation methods but is not significant.
Table 2
Comparing the posttrait and poststate anxiety scores in three studied groups including systematic desensitization, Benson's relaxation, and control
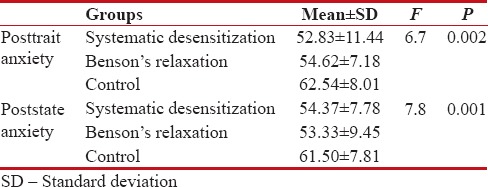
|
Table 3 shows the mean changes in trait and state anxiety scores in three groups and these changes were statistically significant. In post hoc analysis, there was no significant difference in two intervention groups. Nevertheless, there was a significant difference between two intervention methods and control group by Tukey test (P < 0 xss=removed>P = 0.013 and −7.5 vs. 0.167, P = 0.023). Moreover, the mean change in state anxiety scores in two intervention groups was more than control group, respectively, and was statistically significant (76.5 vs. −0.625, P = 0.007 and −7.5 vs. −0.625, P = 0.008).
Table 3
Comparing the changes in trait and state anxiety scores in three studied groups including systematic desensitization, Benson's relaxation, and control in pre- and post-intervention
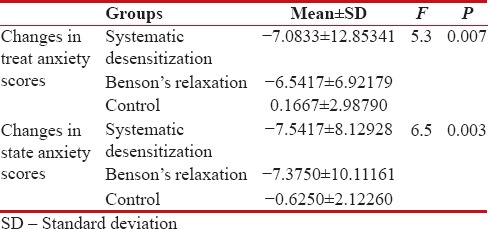
|
Discussion
Based on our results, Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization were effective methods for decreasing in the nurses’ anxiety in both state and trait dimensions. Moreover, there was no significant difference between two intervention methods regarding state and trait anxiety. Nevertheless, the mean of changes in anxiety score was higher in the systematic desensitization. The staff in medical workplaces are exposed to a variety of stresses and high risk for anxiety disorders. Therefore, delay in primary prevention, early diagnosis, and control of anxiety disorder caused continually of psychological effects. Furthermore, preventive methods for control and decreasing of anxiety are important.[26] The effects of different methods were used for control or improvement in the anxiety of nurses or patients in some studies.[16,17,27,28,29,30]
Desensitization training for declining of anxiety was used in one of the intervention groups in the current study, and our results showed a higher level of anxiety in control group than desensitization group. Similar results observed in Maredpour et al.'s study that the systematic desensitization was effective on examination stress of male students[22] and Rajiah and Saravanan's study in reduce test anxiety among 1st-year pharmacy students.[3] However, systematic desensitization exposed the physiological and cognitive aspects of people could decrease the stress or anxiety. Muscular relaxation with training of the stressful situations prevents from the unwilling reactions and acts as a new response for recent stressful stimulants.[22] Moreover, in systematic desensitization, the individuals trained about the methods of relaxation regarding the environmental pressures and caused to prevent from disturbing physiological effects.[31]
In the current study, Benson's relaxation was effective in the anxiety level of nurses in comparing to the control group. This method was used in Mahdavi et al.'s study and in that showed changes in perceived stress, anxiety, and depression of hemodialysis patients.[18] Other studies conducted for decreasing stress and anxiety by Benson's relaxation in rheumatoid arthritis patients,[28] patients awaiting abdominal surgery,[32] women undergoing breast biopsy,[33] and patients with rheumatoid arthritis patients[28] and for pain and quality of life of hemodialysis patients.[21] In another study, the skill training program was effective in decreasing the anxiety and improving general health status of homemaker women.[34]
However, there are different methods for relaxation that could be effective on anxiety or pain decreasing or improvement in quality of life and happiness. Nevertheless, Benson's relaxation method is more common and acceptable in comparing other method due to the simple education and training and is effective on the different scope of symptoms including pain, anxiety, depression, self-stem, self-efficacy, and quality of life.[13,18,20,21,28] These effect due to the effect of relaxation on the hypothalamus and decreasing in the sympathetic nervous system and catecholamine and consequently balance in heart rate, pulse rate, respiratory, and muscular spasms.[13,35]
Our results showed a significant difference between before and after of intervention in two intervention methods of relaxation. Based on the recent of other study, the relaxation methods have not any side effect on the nurses and could be effective on the anxiety of nurse in the workplaces. However, these methods are more effective when conducted in the peace places with positive attitude and in comfortable situations.[14]
Conclusion
Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization are effective methods in decreasing the anxiety of nurses that worked in the medical places. Both methods could be effective in improvement of the state and trait dimensions of anxiety. Moreover, there was no significant difference between Benson's relaxation and systematic desensitization methods in decreasing of the state and trait anxiety. However, these methods could be applied in stressful situation among medical staffs of students.
Financial support and sponsorship
This study was supported by Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the research center of Arak University of Medical Sciences. They are also grateful nurses who participated in this study. This article is extracted from the thesis of Miss. Khatereh Goudarzi, the student of Master of Sciences (MSc) in nursing major. It is financially was supported by grant number 2376 in Research Vice-Chancellor of Arak University of Medical Sciences.
References
- Patterson SL. The effect of emotional freedom technique on stress and anxiety in nursing students: A pilot study. Nurse Educ Today 2016;40:104-10.
- Bayati A, Beigi M, Salehi M. Depression prevalence and related factors in Iranian students. Pak J Biol Sci 2009;12:1371-5.
- Rajiah K, Saravanan C. The effectiveness of psychoeducation and systematic desensitization to reduce test anxiety among first-year pharmacy students. Am J Pharm Educ 2014;78:163.
- Sun FK, Long A, Tseng YS, Huang HM, You JH, Chiang CY. Undergraduate student nurses' lived experiences of anxiety during their first clinical practicum: A phenomenological study. Nurse Educ Today 2016;37:21-6.
- Szpak JL, Kameg KM. Simulation decreases nursing student anxiety prior to communication with mentally ill patients. Clin Simul Nurs 2013;39:e13-9.
- Zweers D, de Graaf E, Teunissen SC. Non-pharmacological nurse-led interventions to manage anxiety in patients with advanced cancer: A systematic literature review. Int J Nurs Stud 2016;56:102-13.
- Mohammadbeigi A, Absari R, Valizadeh F, Saadati M, Sharifimoghadam S, Ahmadi A, et al. Sleep quality in medical students; the impact of over-use of mobile cell-phone and social networks. J Res Health Sci 2016;16:46-50.
- Hansen AB, Stayner L, Hansen J, Andersen ZJ. Night shift work and incidence of diabetes in the Danish Nurse Cohort. Occup Environ Med 2016;73:262-8.
- Chen Y, Yang X, Wang L, Zhang X. A randomized controlled trial of the effects of brief mindfulness meditation on anxiety symptoms and systolic blood pressure in Chinese nursing students. Nurse Educ Today 2013;33:1166-72.
- Mayer J, Salovey P. Emotional intelligence. Imagin Cogn Pers 2009;9:185-211.
- Piquette D, Reeves S, LeBlanc VR. Stressful intensive care unit medical crises: How individual responses impact on team performance. Crit Care Med 2009;37:1251-5.
- Moshiri E, Modir H, Bagheri N, Mohammadbeigi A, Jamilian H, Eshrati B. Premedication effect of dexmedetomidine and alfentanil on seizure time, recovery duration, and hemodynamic responses in electroconvulsive therapy. Ann Card Anaesth 2016;19:263-8.
- Elali ES, Mahdavi A, Jannati Y, Yazdani J, Setareh J. Effect of benson relaxation response on stress among in hemodialysis patients. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci 2012;22:61-8.
- van Dixhoorn J, White A. Relaxation therapy for rehabilitation and prevention in ischaemic heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2005;12:193-202.
- Zakerimoghadam M, Shaban M, Mehran A, Hashemi S. Effect of muscle relaxation on anxiety of patients undergo cardiac catheterization. Hayat 2010;16:64-71.
- ;Day RC, Sadek SN. The effect of Benson's relaxation response on the anxiety levels of Lebanese children under stress. J Exp Child Psychol 1982;34:350-6.
- Heidari Gorji MA, Davanloo AA, Heidarigorji AM. The efficacy of relaxation training on stress, anxiety, and pain perception in hemodialysis patients. Indian J Nephrol 2014;24:356-61.
- Mahdavi A, Gorji MA, Gorji AM, Yazdani J, Ardebil MD. Implementing benson's relaxation training in hemodialysis patients: Changes in perceived stress, anxiety, and depression. N Am J Med Sci 2013;5:536-40.
- Wang F, Lee EK, Wu T, Benson H, Fricchione G, Wang W, et al. The effects of tai chi on depression, anxiety, and psychological well-being: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Behav Med 2014;21:605-17.
- Rambod M, Pourali-Mohammadi N, Pasyar N, Rafii F, Sharif F. The effect of Benson's relaxation technique on the quality of sleep of Iranian hemodialysis patients: A randomized trial. Complement Ther Med 2013;21:577-84.
- Rambod M, Sharif F, Pourali-Mohammadi N, Pasyar N, Rafii F. Evaluation of the effect of Benson's relaxation technique on pain and quality of life of haemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud 2014;51:964-73.
- Maredpour A, Jahanbakhsh Ganjeh S, Hossininik S. The effectiveness of stress inoculation training, systematic desensitization, and a combined approach on test anxiety, academic performance and self-efficacy of male university students. Res Cogn Behav Sci 2011;1:59-72.
- Spielberger, C D. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology. Wiley Online Library. 2010.
- Spielberger CD. STAI manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory, self-evaluation questionnaire. Consulting Psychologists Press; 1970. p. 1-24.
- Abdekhodae M, Mahram B, Eyzanloo Z. Relationship between perfectionism and state anxiety in student. Res Clin Psychol Couns2011;1:47-58.
- Ebrahimi Iraqi Nezhad Z, Tol A, Shojaeezadeh D, Khorsandi M, Bagheri F. Effectiveness of PRECEDE model for health education on anxiety of nurses employed in hospitals of Arak University of Medical Sciences: Application of PRECEDE model constructs anxiety of nurses and PRECEDE model. J Health Syst Res 2014;10:752-65.
- Aitken JR, Benson JW. The use of relaxation/densensitization in treating anxiety associated with flying. Aviat Space Environ Med 1984;55:196-9.
- Bagheri-Nesami M, Mohseni-Bandpei MA, Shayesteh-Azar M. The effect of Benson relaxation technique on rheumatoid arthritis patients: Extended report. Int J Nurs Pract 2006;12:214-9.
- Demircelik MB, Yigit D, Sentepe E, Keklik M, Cetın M, Cetın Z, et al. The effectiveness of multimedia nursing education on reducing illness-related anxiety and depression in coronary care unit's patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;62:C50.
- Islekdemir B, Kaya N. Effect of family presence on pain and anxiety during invasive nursing procedures in an emergency department: A randomized controlled experimental study. Int Emerg Nurs 2016;24:39-45.
- Spielberger CD, Anton WD, Bedell J. The nature and treatment of test anxiety. Emotions and Anxiety: New Concepts, Methods, and Applications. London, New York: Psychology Press; 2015. p. 317-44.
- Nikbakht Nasrabadi AR, Taghavi Larijani T, Mahmoudi M, Taghlili F. A comparative study of the effect of Benson's relaxation technique and zekr (rosary) on the anxiety level of patients awaiting abdominal surgery. Hayat 2004;10:29-37.
- Park ER, Traeger L, Willett J, Gerade B, Webster A, Rastegar S, et al. Arelaxation response training for women undergoing breast biopsy: Exploring integrated care. Breast 2013;22:799-805.
- Mohammadbeigi A, Seyedi S, Behdari M, Brojerdi R, Rezakhoo A. The effect of life skills training on decreasing violence and general health promotion of women. J Nurs Midwifery Urmia Univ Med Sci 2016a;13:903-11.
- Chang BH, Casey A, Dusek JA, Benson H. Relaxation response and spirituality: Pathways to improve psychological outcomes in cardiac rehabilitation. J Psychosom Res 2010;69:93-100.
References
- Patterson SL. The effect of emotional freedom technique on stress and anxiety in nursing students: A pilot study. Nurse Educ Today 2016;40:104-10.
- Bayati A, Beigi M, Salehi M. Depression prevalence and related factors in Iranian students. Pak J Biol Sci 2009;12:1371-5.
- Rajiah K, Saravanan C. The effectiveness of psychoeducation and systematic desensitization to reduce test anxiety among first-year pharmacy students. Am J Pharm Educ 2014;78:163.
- Sun FK, Long A, Tseng YS, Huang HM, You JH, Chiang CY. Undergraduate student nurses' lived experiences of anxiety during their first clinical practicum: A phenomenological study. Nurse Educ Today 2016;37:21-6.
- Szpak JL, Kameg KM. Simulation decreases nursing student anxiety prior to communication with mentally ill patients. Clin Simul Nurs 2013;39:e13-9.
- Zweers D, de Graaf E, Teunissen SC. Non-pharmacological nurse-led interventions to manage anxiety in patients with advanced cancer: A systematic literature review. Int J Nurs Stud 2016;56:102-13.
- Mohammadbeigi A, Absari R, Valizadeh F, Saadati M, Sharifimoghadam S, Ahmadi A, et al. Sleep quality in medical students; the impact of over-use of mobile cell-phone and social networks. J Res Health Sci 2016;16:46-50.
- Hansen AB, Stayner L, Hansen J, Andersen ZJ. Night shift work and incidence of diabetes in the Danish Nurse Cohort. Occup Environ Med 2016;73:262-8.
- Chen Y, Yang X, Wang L, Zhang X. A randomized controlled trial of the effects of brief mindfulness meditation on anxiety symptoms and systolic blood pressure in Chinese nursing students. Nurse Educ Today 2013;33:1166-72.
- Mayer J, Salovey P. Emotional intelligence. Imagin Cogn Pers 2009;9:185-211.
- Piquette D, Reeves S, LeBlanc VR. Stressful intensive care unit medical crises: How individual responses impact on team performance. Crit Care Med 2009;37:1251-5.
- Moshiri E, Modir H, Bagheri N, Mohammadbeigi A, Jamilian H, Eshrati B. Premedication effect of dexmedetomidine and alfentanil on seizure time, recovery duration, and hemodynamic responses in electroconvulsive therapy. Ann Card Anaesth 2016;19:263-8.
- Elali ES, Mahdavi A, Jannati Y, Yazdani J, Setareh J. Effect of benson relaxation response on stress among in hemodialysis patients. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci 2012;22:61-8.
- van Dixhoorn J, White A. Relaxation therapy for rehabilitation and prevention in ischaemic heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2005;12:193-202.
- Zakerimoghadam M, Shaban M, Mehran A, Hashemi S. Effect of muscle relaxation on anxiety of patients undergo cardiac catheterization. Hayat 2010;16:64-71.
- ;Day RC, Sadek SN. The effect of Benson's relaxation response on the anxiety levels of Lebanese children under stress. J Exp Child Psychol 1982;34:350-6.
- Heidari Gorji MA, Davanloo AA, Heidarigorji AM. The efficacy of relaxation training on stress, anxiety, and pain perception in hemodialysis patients. Indian J Nephrol 2014;24:356-61.
- Mahdavi A, Gorji MA, Gorji AM, Yazdani J, Ardebil MD. Implementing benson's relaxation training in hemodialysis patients: Changes in perceived stress, anxiety, and depression. N Am J Med Sci 2013;5:536-40.
- Wang F, Lee EK, Wu T, Benson H, Fricchione G, Wang W, et al. The effects of tai chi on depression, anxiety, and psychological well-being: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Behav Med 2014;21:605-17.
- Rambod M, Pourali-Mohammadi N, Pasyar N, Rafii F, Sharif F. The effect of Benson's relaxation technique on the quality of sleep of Iranian hemodialysis patients: A randomized trial. Complement Ther Med 2013;21:577-84.
- Rambod M, Sharif F, Pourali-Mohammadi N, Pasyar N, Rafii F. Evaluation of the effect of Benson's relaxation technique on pain and quality of life of haemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud 2014;51:964-73.
- Maredpour A, Jahanbakhsh Ganjeh S, Hossininik S. The effectiveness of stress inoculation training, systematic desensitization, and a combined approach on test anxiety, academic performance and self-efficacy of male university students. Res Cogn Behav Sci 2011;1:59-72.
- Spielberger, C D. State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology. Wiley Online Library. 2010.
- Spielberger CD. STAI manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory, self-evaluation questionnaire. Consulting Psychologists Press; 1970. p. 1-24.
- Abdekhodae M, Mahram B, Eyzanloo Z. Relationship between perfectionism and state anxiety in student. Res Clin Psychol Couns2011;1:47-58.
- Ebrahimi Iraqi Nezhad Z, Tol A, Shojaeezadeh D, Khorsandi M, Bagheri F. Effectiveness of PRECEDE model for health education on anxiety of nurses employed in hospitals of Arak University of Medical Sciences: Application of PRECEDE model constructs anxiety of nurses and PRECEDE model. J Health Syst Res 2014;10:752-65.
- Aitken JR, Benson JW. The use of relaxation/densensitization in treating anxiety associated with flying. Aviat Space Environ Med 1984;55:196-9.
- Bagheri-Nesami M, Mohseni-Bandpei MA, Shayesteh-Azar M. The effect of Benson relaxation technique on rheumatoid arthritis patients: Extended report. Int J Nurs Pract 2006;12:214-9.
- Demircelik MB, Yigit D, Sentepe E, Keklik M, Cetın M, Cetın Z, et al. The effectiveness of multimedia nursing education on reducing illness-related anxiety and depression in coronary care unit's patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;62:C50.
- Islekdemir B, Kaya N. Effect of family presence on pain and anxiety during invasive nursing procedures in an emergency department: A randomized controlled experimental study. Int Emerg Nurs 2016;24:39-45.
- Spielberger CD, Anton WD, Bedell J. The nature and treatment of test anxiety. Emotions and Anxiety: New Concepts, Methods, and Applications. London, New York: Psychology Press; 2015. p. 317-44.
- Nikbakht Nasrabadi AR, Taghavi Larijani T, Mahmoudi M, Taghlili F. A comparative study of the effect of Benson's relaxation technique and zekr (rosary) on the anxiety level of patients awaiting abdominal surgery. Hayat 2004;10:29-37.
- Park ER, Traeger L, Willett J, Gerade B, Webster A, Rastegar S, et al. Arelaxation response training for women undergoing breast biopsy: Exploring integrated care. Breast 2013;22:799-805.
- Mohammadbeigi A, Seyedi S, Behdari M, Brojerdi R, Rezakhoo A. The effect of life skills training on decreasing violence and general health promotion of women. J Nurs Midwifery Urmia Univ Med Sci 2016a;13:903-11.
- Chang BH, Casey A, Dusek JA, Benson H. Relaxation response and spirituality: Pathways to improve psychological outcomes in cardiac rehabilitation. J Psychosom Res 2010;69:93-100.


 PDF
PDF  Views
Views  Share
Share

